Urban Agriculture
Overview
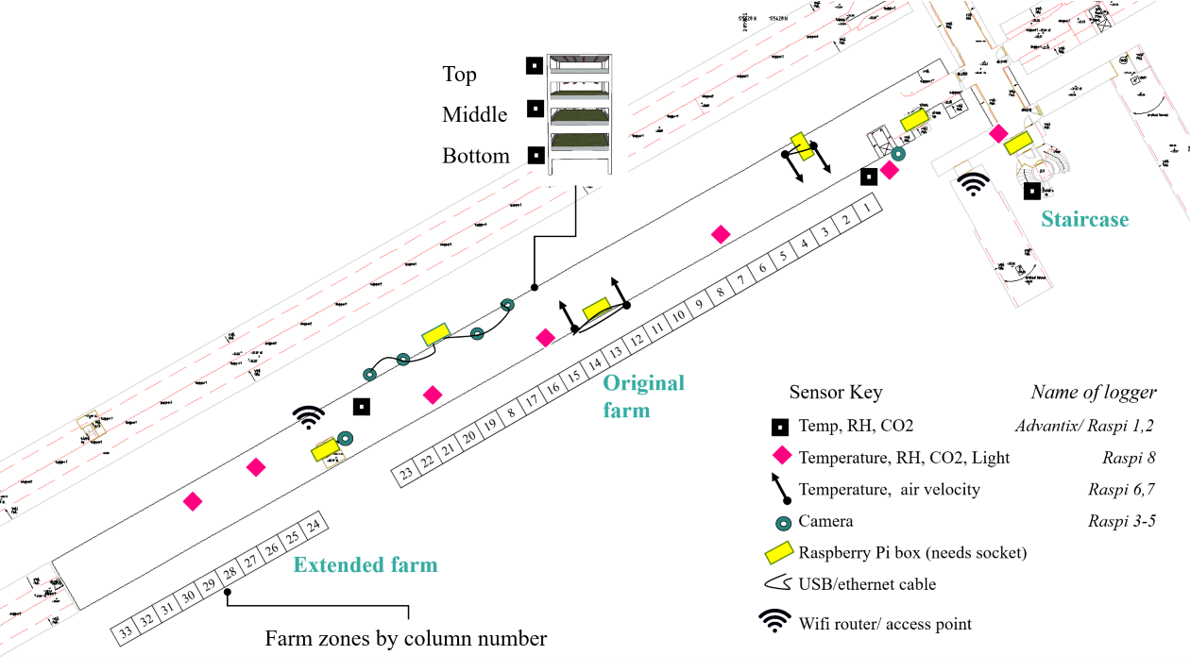
The urban agriculture project investigates various digital tools to optimise the resource use efficiency of integrating greenhouses in the built environment.
Known as urban-integrated agriculture, vertical farming, controlled environment agriculture, this concept is gaining increasing traction by investors, start-ups and city planners alike. Integrating a greenhouse in a city can provide multiple benefits: its high yields contribute to local food production, provide local employment with its year-round harvests, increases urban self-sufficiency. However, several issues need to be addressed for its further sustainable development. For instance, high yields come at a high energy cost. The increased resource demand of urban farming may require re-thinking of our food distribution systems, and delivery of water, nutrients and energy to cities.
Digital tools can help answer some of these questions. By better understanding the complicated interdepencies between the built environment and plants, we can predict energy demand, crop yields, and improve day to day operational efficiency. Given the numerous unknowns about these systems, data-centric methods represent an opportunity to learn about these novel systems, and can provide decision-making assistance along the way too.
Click on the link of these three projects to find out more about the tools developed.